A Survey on the Use of Blockchain for Future 6G: Technical Aspects, Use Cases, Challenges and Research Directions – Researchgate
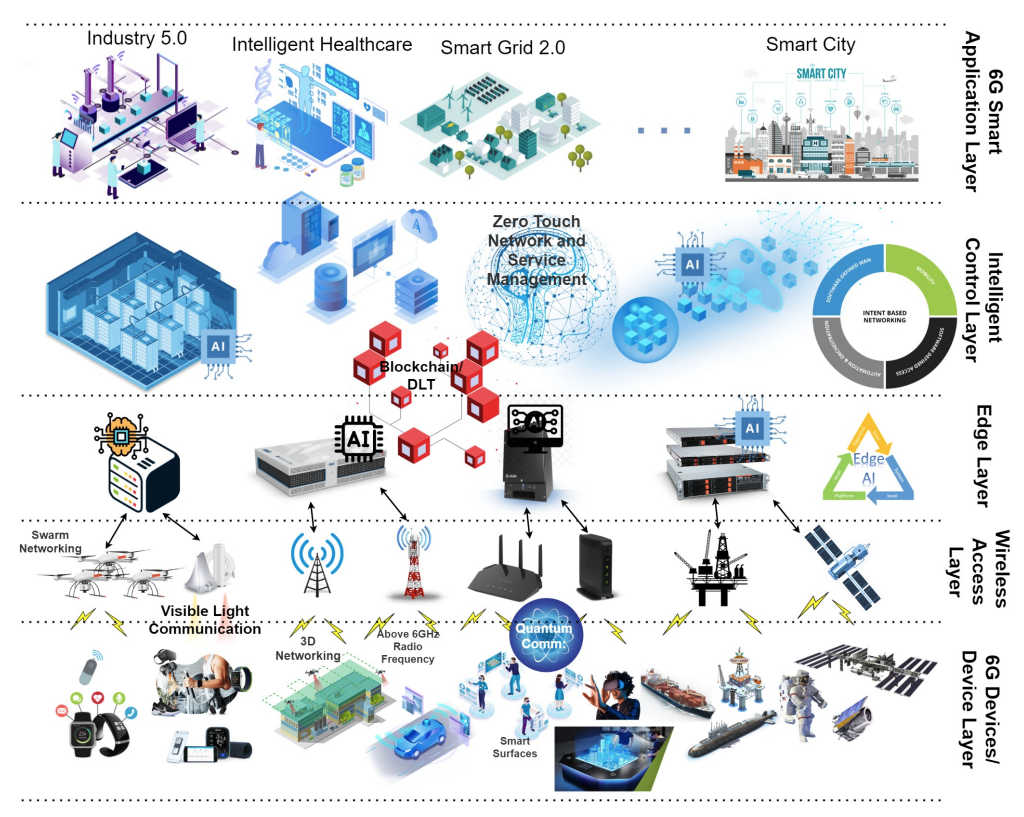
We present a high-level view of the role of blockchain for 6G trends
and requirements. Following that, we conduct an in-depth study
on how the blockchain can provide a secure, transparent, and
decentralised underpinning to various technical aspects and use
cases of 6G. Thereafter, we discuss the deployment challenges
to be faced
Impact of Blockchain Technology in 6G Network: A Comprehensive survey – IEEE
6G offers superior reliability,
speed, latency and ubiquity. However, resource allocation is a priority thanks to the scarcity of spectrum, while security is an essential feature. Blockchain could establish secure communication in 6G networks as well as managing the resource allocation and sharing process.
BEAT: Blockchain-Enabled Accountable Infrastructure Sharing in 6G and Beyond – Arxiv
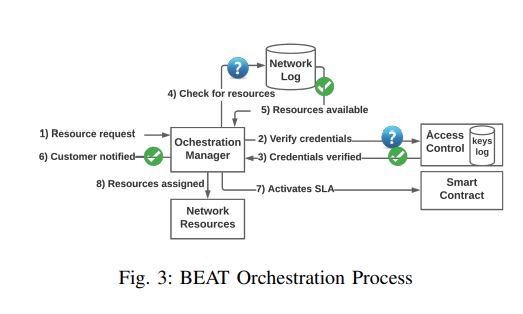
The primary challenges for future technologies are not just low-latency and high-bandwidth. The more critical problem Mobile Service Providers (MSPs) will face will be in balancing the inflated demands of network connections and customers’ trust in the network service, that is, being able to interconnect billions of unique devices while adhering to the agreed terms of Service Level Agreements (SLAs). To meet these targets, it is self-evident that MSPs cannot operate in a solitary environment. They must enable cooperation among themselves in a manner that ensures trust, both between themselves as well as with customers. In this study, we present the BEAT (Blockchain Enabled Accountable and Transparent) Infrastructure Sharing architecture. BEAT exploits the inherent properties of permissioned type of distributed ledger technology (i.e., permissioned distributed ledgers) to deliver on accountability and transparency metrics whenever infrastructure needs to be shared between providers. We also propose a lightweight method that enables device-level accountability.
Empowering digital supply chain transformation by utilizing Industry 4.0, Smart Factories, Standards, Smart Contracts and Blockchains

As complex supply chains respond to unexpected shocks, the collection and sharing of data is becoming more urgent and complicated, both to uphold contracts and to enable flexibility. The University of Derby’s Raj Thakar proposes how this might be handled.
Engineering Bites, November 2020
Smart Cities, NFV, Data Security and fixing AI systems all provide delicious, nutritious brain-food in this month’s edition.